
Cabling infrastructure
Cabling infrastructure is the organized system of cables, connectors, and other hardware used to transmit voice, data, and video signals throughout a building or campus.

Cabling infrastructure is the organized system of cables, connectors, and other hardware used to transmit voice, data, and video signals throughout a building or campus.
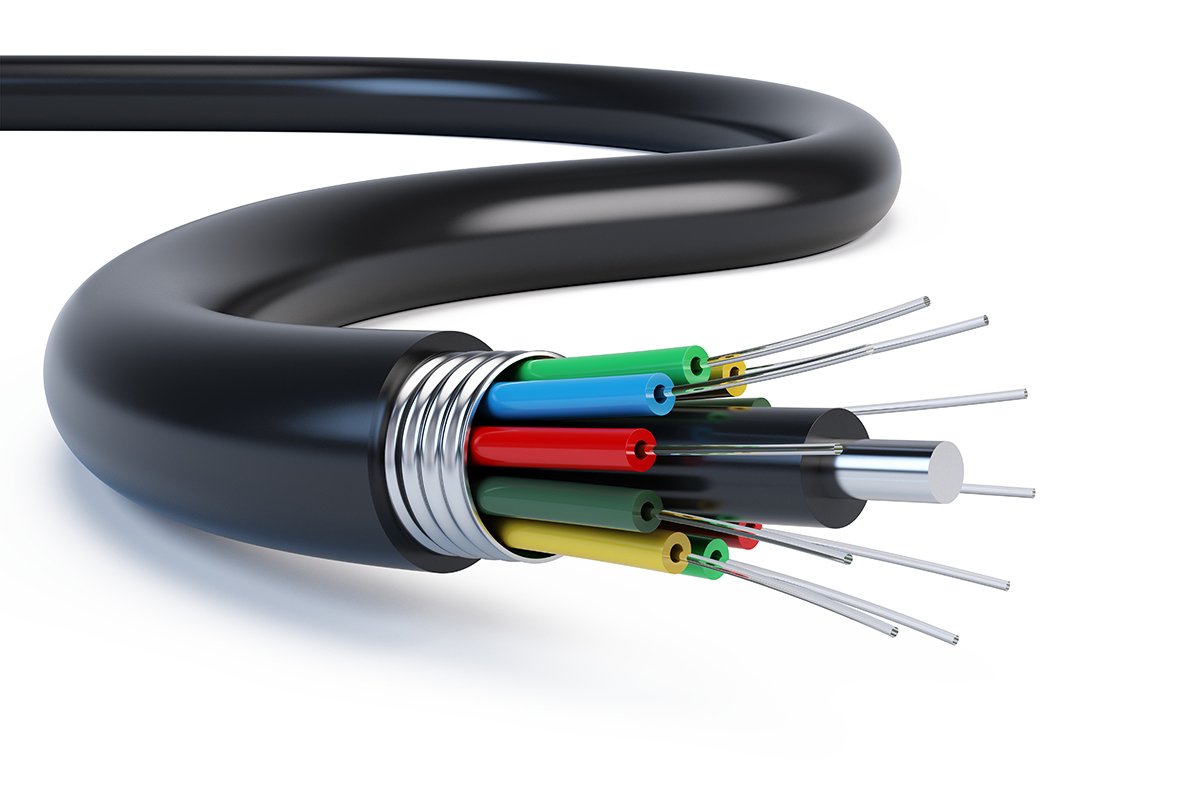
Fiber infrastructure refers to a network of fiber-optic cables that transmits data using pulses of light, forming the backbone of modern high-speed communication.

"Tools & Tester" can refer to both Information and Communications Technology (ICT) hardware installation/maintenance tools and specialized In-Circuit Test (ICT) equipment used in electronics manufacturing.

Power management is a broad term referring to strategies, technologies, and systems designed to monitor, control, and optimize the consumption and distribution of electrical power.

A "smart solution" is a technology-based approach that integrates devices, data processing, and automation to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance user experience across various applications, from homes to entire cities.

Cabling infrastructure is the organized system of cables, connectors, and other hardware used to transmit voice, data, and video signals throughout a building or campus.

Fiber infrastructure refers to a network of fiber-optic cables that transmits data using pulses of light, forming the backbone of modern high-speed communication.

"Tools & Tester" can refer to both Information and Communications Technology (ICT) hardware installation/maintenance tools and specialized In-Circuit Test (ICT) equipment used in electronics manufacturing.

Power management is a broad term referring to strategies, technologies, and systems designed to monitor, control, and optimize the consumption and distribution of electrical power.

A "smart solution" is a technology-based approach that integrates devices, data processing, and automation to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance user experience across various applications, from homes to entire cities.
• Compliant to TIA-568.2-D Category 6A cable specifications
• 23 AWG SOLID-Bare Copper Conductor
• Characterized and tested up to 250MHz
• 4 Pair with LSZH Outer Jacket
• ROHS Compliant & UL Approval, DELTA, GHMT
• Print legend contains footage marking from 305M to 001M
Products Characteristics
• Conductor Diameter: 0.57mm ± 0.008mm
• Foam PE Insulation: 1.34mm ± 0.03 mm
• Al foil:Overlap rate≥125%
• Braiding:16*6*0.12mm ALMG
• Drain wire:1*0.4 tinned copper
• Outer Jacket Thickness: 0.5mm±0.5mm
• External Diameter: 7.9mm±0.5mm
• Linear Resistance: Max.<85 Ω/km
• Mutual Capacity (nom.): 5.6nF/100M
• Unbalance Capacity Max (p/p at 1 KHz): 1600 pF/km
• Characteristic Impedance (1 to 100 MHz): 100 ±15Q
• Velocity OF Propagation (f>1 MHz): 69% of c
Application
• IEEE 802.3: 10G BASE-T (Gigabit Ethernet), 100BASE-TX, 10BASE-T
• ANSI/TIA/EIA-854: 10G BASE-TX
• 155 Mb/s, 1.2 Gb/s ATM
• ANSI X3.263: 100 Mb/s
• IEEE 802.3af DTE Power (POE)
• 4/16 Mb/s Token Ring
• Digital Video
• Broadband and Baseband Analog Video
Complied Standards
• ISO/IEC 11801:2011(Ed.2.2)
• IEC 61156-5:2009(Ed.2.0)
• EN 50173-1:2011
• EN 50173-2:2007 including amendment A1:2010
• ANSI/TIA-568-C.2:2009
• TIA/EIA-568B.2-2001
| Reference Electrical Characteristics | ||||||
| Frequency (MHz) | Return loss(dB) | Attenuation {dB/100m) | NEXT (dB) | PSNEXT (dB) | ELFEXT (dB) | PSELFEXT (dB) |
| 1 | 20 | 2 | 74.3 | 72.3 | 67.8 | 64.8 |
| 4 | 23 | 3.80 | 65.3 | 63.3 | 55.8 | 52.8 |
| 10 | 25 | 5.30 | 59.3 | 57.3 | 47.8 | 44.8 |
| 20 | 25 | 8.50 | 54.8 | 52.2 | 41.8 | 38.8 |
| 62.5 | 21.5 | 15.40 | 47.4 | 45.4 | 42 | 29.1 |
| 100 | 20.1 | 19.80 | 44.3 | 42.3 | 27.8 | 25 |
| 150 | 18.9 | 24.70 | 41.7 | 39.7 | 24.3 | 21.3 |
| 200 | 18 | 29 | 39.8 | 37.8 | 21.8 | 19 |
| 250 | 17.3 | 32.8 | 38.3 | 36.3 | 20.4 | 17 |

Cabling infrastructure is the organized system of cables, connectors, and other hardware used to transmit voice, data, and video signals throughout a building or campus.

Fiber infrastructure refers to a network of fiber-optic cables that transmits data using pulses of light, forming the backbone of modern high-speed communication.

"Tools & Tester" can refer to both Information and Communications Technology (ICT) hardware installation/maintenance tools and specialized In-Circuit Test (ICT) equipment used in electronics manufacturing.

Power management is a broad term referring to strategies, technologies, and systems designed to monitor, control, and optimize the consumption and distribution of electrical power.

A "smart solution" is a technology-based approach that integrates devices, data processing, and automation to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance user experience across various applications, from homes to entire cities.

Cabling infrastructure is the organized system of cables, connectors, and other hardware used to transmit voice, data, and video signals throughout a building or campus.

Fiber infrastructure refers to a network of fiber-optic cables that transmits data using pulses of light, forming the backbone of modern high-speed communication.

"Tools & Tester" can refer to both Information and Communications Technology (ICT) hardware installation/maintenance tools and specialized In-Circuit Test (ICT) equipment used in electronics manufacturing.

Power management is a broad term referring to strategies, technologies, and systems designed to monitor, control, and optimize the consumption and distribution of electrical power.

A "smart solution" is a technology-based approach that integrates devices, data processing, and automation to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance user experience across various applications, from homes to entire cities.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.